Classification is the process of organizing or grouping things based on their similarities and shared characteristics. Binomial nomenclature is a system that names organisms using two parts: the genus first and the species second.
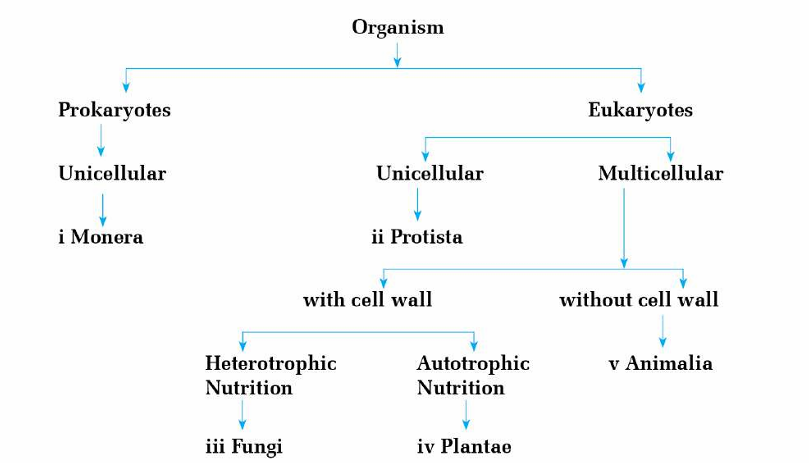
Five Kingdom system of classification is more scientific and appropriate than two kingdom system of classification because of the following reasons.
- Unicellular and multicellular organisms are separated.
- Organisms having prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells are separated.
- Green plants and non-green plants are separated.
- This system of classification is based on evolutionary trend of living organisms.
Kingdom Plantae
Division Algae
Algae consist of large group of simple aquatic organisms that are capable of photosynthesis.
Examples: Chlamydomonas, Volvox, Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Fucus etc.
Characteristics
- The are either unicellular (Chlamydomonas) or multicellular (Spirogyra)
- They are autotrophs due to the presence of chlorophyll.
- Their cell wall is composed of cellulose.
- They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Division Bryophyta
Bryophytes consist of non-vascular land plants that are commonly known as mosses, liverworts, and hornworts. Examples: Marchantia (liverworts), moss, Riccia, etc.
Characteristics
- They are multicellular plants.
- They are autotrophs.
- Plant body is either thallus or differentiated into rhizoid, stem and simple leaf.
- Vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) are absent.
- They show alternation of generation in their life cycle.
Division Tracheophyta
Well developed plants having vascular tissues are kept in division Tracheophyta. Division Tracheophyta is further divided into three sub-divisions. They are as follows:
Sub division Pteridophyta
Pteridophyta is a subdivision of vascular plants that reproduce by spores and have an alternation of generations. Examples: Fern, Lycopodium, Horsetail (Equisetum), fiddlehead fern, Ground gooseberry, Selaginaella, Pteris etc.
Characteristics
- They have no seed but plant body is divided into roots, stem (rhizome) and leaves.
- Vascular tissues (xylem and phloem) are present.
- They are autotrophs
- They show alternation of generation in their life cycle.
Sub division Gymnosperms
Gymnosperms are seed-producing plants that do not have flowers or fruits. Examples: Cycas, Pinus, Juniper, Himalayan yew, Himalayan cedar.
Characteristics
- They bear cones instead of flowers Male cones and female cones are separate.
- There is no ovary in cone and hence no fruits. Seed is naked.
- Their leaves are elongated and needle like.
Sub division Angiosperm
Angiosperms are the most diverse and dominant group of land plants that bear flowers and fruits. Examples: Maize, banana, paddy, soybean, Lemna, water hyacinth, Pistia, rose, apple, mustard, sugarcane, onion, garlic, orange, mango, Sal, sissoo, simal,
Characteristics:
- They have well developed root, stem, leaf, flower and fruit.
- These plants contain seeds inside the fruit.
- They bear real flower and flower contains both ovary and ovule.
On the basis of number of cotyledons present in a seed, division Angiosperms is divided into two classes. They are as follows:
Monocotyledons:
The flowering plants having only one cotyledon in their seeds are called monocotyledons. Examples: Wheat, sugarcane, banana, barley, bamboo, onion, garlic, grass, paddy, etc.
Characteristics:
- A seed contains only one cotyledon.
- They have parallel venation in leaves.
- They have fibrous root.
Dicotyledons:
The flowering plants having two cotyledons in their seeds are called dicotyledons. Examples: Rose, mango, apple, bean, pea, mustard, orange, lotus, sunflower, soybean, gram, pumpkin, etc.
Characteristics:
- A seed contains two cotyledons.
- They have reticulate venation in leaves.
- They have tap root system.
Kingdom Animalia
Invertebrates
Invertebrates are those animals that do not have a backbone or a vertebral column. On the basis of structure and development, invertebrates are classified into eight phyla.
Characteristics:
- They do not have backbone or vertebral column.
- Their organs and system are less developed.
- They are found in water, land and air.
Phylum Porifera
Porifera are considered the simplest among multicellular animals and they lack true organs. They are commonly found in fresh and marine water. Examples: Leucosolenia, Hylonema, Cliona, Sycon, Spongilla, Euspongia.
Characteristics:
- They are first multicellular organisms.
- They have numerous pores in their body.
- They respire through general body surface.
- They are diploblastic animals.
Phylum Coelenterata
Coelenterates are aquatic invertebrates having hollow body cavity called coelenteron. They are found in fresh and marine water. Example: Hydra, Coral, Jellyfish, Sea anemone, etc.
Characteristics:
- They are multicellular and diploblastic animals.
- Mouth is surrounded by tentacles.
- They respire through general body surface.
- They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Platyhelminthes are commonly known as flatworms or tapeworms. They are mostly parasitic found in bodies of other animals. Examples: Liverfluke, Tapeworm, Diplozoon, Otoplana, Blood fluke, Planaria.
Characteristics:
- Their body is flat leaf-like or long ribbon like. Suckers are present.
- They are triploblastic animals.
- They do not have well developed organ system.
- They respire through general body surface.
- They reproduce both sexually and asexually.
Phylum Nemathelminthes
Nemathelminthes are commonly called thread worm or round worm. They are mostly parasitic and suck blood from humans and other animals. Examples: Roundworm (Ascaris), Hook worm, Pinworm.
Characteristics:
- They have cylindrical and elongated body with tapering ends.
- They are triploblastic animals.
- They have developed digestive system with mouth, anus and sucker.
- Their respiratory and circulatory systems are absent.
- They reproduce by sexual methods.
Phylum Annelida
phylum Annelida is a group of segmented worms having rings in their bodies. They are found in water, soil and sand. Examples: earthworm, leeches, Nereis, sandworm, etc.
- Their body is elongated, cylindrical and segmented both internally and externally.
- The body is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic.
- They respire through outer body surface.
- Digestive system and circulatory system is well developed.
- These animals may be unisexual or bisexual.
Phylum Arthropoda
Arthropoda is the largest phylum of invertebrates with jointed legs and exoskeleton. They are found on land, air and water. Examples: Crab, Butterfly, Prawn, Grasshopper, Ant, Honeybee, Moth, Spider, Scorpion, etc.
Characteristics:
- Their body is divisible into the head, thorax and abdomen.
- The body is bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and segmented.
- They have sexual reproduction. Male and female are separate.
- They breathe through skin, gills or trachea.
Phylum Mollusca
Mollusca are a diverse group of animals with soft body, shells and a muscular foot. They are found in water and moist soil. Examples: Snail, Slug, Unio, Octopus, cuttlefish, etc.
Characteristics:
- They have soft and unsegmented body.
- They breathe through gills or lungs.
- Their body is asymmetrical.
- The digestive system, circulatory system, and nervous system are developed.
- They are unisexual, but few are hermaphrodite or bisexual.
Phylum Echinodermata
Phylum Echinodermata consists of exclusively marine animals with spiny skins and star-like shapes. Examples: Starfish, Sea cucumber, Sea urchin, Brittle star, etc.
Characteristics:
- They have spiny skin.
- They do not have distinct head.
- They move with the help of tube feet.
- They are triploblastic and radially symmetrical animals.
- They are unisexual and reproduce sexually. Regeneration is common in them.
Phylum Chordata
Phylum Chordata consist of those animals having notochord. It consist of most advanced animals of animal kingdom. It is further divided into four sub-phyla. They are
- Sub-phylum Hemichordata
- Sub-phylum Urochordata
- Sub-phylum Cephalochordata
- Sub-phylum Vertebrata
Characteristics of Chordata
- They develop gills in embryonic stage.
- They have a hollow tubular nerve cord just above the notochord.
- They have a closed circulatory system.
Sub Phylum vertebrata
Those animals having vertebral column are called vertebrates.
Characteristics:
- Their body is bilaterally symmetrical.
- The respiration takes place through gills or moist skin or lungs.
- They have well developed circulatory system.
Cold blooded animals
Cold-blooded animals are those animals whose body temperature changes with the environment. They cannot regulate their internal body temperature, so it fluctuates based on the temperature of their surroundings. Examples include reptiles, amphibians, and fish.
Warm blooded animals
These are animals that can maintain a constant internal body temperature regardless of the temperature of their environment. They can regulate their body temperature through metabolic processes. Examples include birds and mammals.
Based on their physical structure and development, animals in sub-phylum vertebrata are divided into five classes: pisces, amphibian, reptilia, aves and mammalia
Pisces
Pisces are permanently aquatic vertebrates that has gills for respiration. Examples: All fishes, sea horse etc
Characteristics
- Their body is elongated, flat and streamlined. Their bodies are covered by scales.
- Their body is distributed into a head, trunk and tail.
- They swim with the help of their tail.
- The gills help in respiration.
- The sexes are separate.
- These are cold-blooded organisms.
Amphibia
The vertebrates that can live both on land and in water are called amphibians. Examples: frogs, toads and salamanders
Characteristics
- Their body is divided into head and trunk. The tail may or may not be present.
- The skin is smooth and rough without any scales, but with glands that make it moist.
- They have two pairs of limbs for locomotion.
- The heart is three chambered.
- Development is indirect with metamorphosis.
Reptiles
Reptiles are a group of cold-blooded animals that have scaly skin and typically lay eggs on land. Examples: snakes, lizards, tortoise and crocodiles.
Characteristics
- They creep or crawl on land.
- Their body can be divided into head, neck, trunk and tail.
- Their body is covered with hard and dry scales.
- Their heart is three chambered.
- They are unisexual animals.
- They have internal fertilization.
Aves
Aves is the class of animals that includes all birds. They are warm-blooded vertebrates with feathers, beaks, and lay eggs. Examples: Crow, Hen, Sparrow, Peacock, Duck, Pigeon, Parrot, Kingfisher,
Characteristics
- Their body is covered with feathers.
- Body is divisible into head, neck, trunk and tail.
- They have very light bones and toothless beak.
- They are warm blooded animals.
- They breathe through lungs.
- They have four chambered heart.
- They are unisexual. Fertilization is internal.
Mammalia
Mammals are warm blooded vertebrates that directly give birth to their young ones. Examples: Cow, Dog, Cat, Elephant, Rhinoceros, Bat, Dolphin, Whale, Lion, Zebra, Monkey, Rabbit, Tiger, etc
Characteristics
- Mammals are warm-blooded animals who give birth to their younger ones.
- They are the most dominant form of animals found in almost all types of habitats.
- They have mammary glands that help them produce milk to feed their younger ones.
- They have pair of external ears.
- Their body remains covered with hair.
- They breathe through lungs.
- Mammals have a four-chambered heart.
Sir, when you are going ko add notes. Holiday is going to end, so I asked
I have added
Sir, tapai le note hamro exam bhanda agadi nai
sabai note add gardinus la sabai. exercise copy bhanda note copy bata dherai padhne try gari ra xu. Ess pali ramro result hunxa bhane ra
And can I say something…